Abstract
Introduction: Predictable pharmacokinetics and fixed dosing regimens of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have simplified venous thromboembolism (VTE) treatment. Rivaroxaban and apixaban both target Factor Xa, yet an important difference lies in their dosing frequency. The impact of twice daily vs once daily DOAC dosing on adherence, and the potential differences on clinical efficacy and safety are unknown. Medication adherence was evaluated in the COBRRA (COmparison of Bleeding Risk between Rivaroxaban and Apixaban) Pilot study (NCT02559856).
Aim: We compared anticoagulation adherence in patients with acute VTE using three different medication adherence assessment tools of variable cost.
Methods: Patients with acute VTE were randomized to apixaban (10 mg twice daily for one week, then 5 mg twice daily) or rivaroxaban (15 mg twice daily for 3 weeks, then 20 mg daily). Participants at the sponsor site (The Ottawa Hospital) had anticoagulation adherence measured using eCAP™, medication diaries, and pill counts. eCAP™ is an electronic prescription bottle cap that records each time the vial is opened to take a tablet. The information was downloaded to a desktop reader at follow up visits to determine medication adherence. Medication diaries were completed by patients and recorded date and time of taking anticoagulant. Pill counts were conducted by the research coordinator at follow up visits and adherence was determined using the following calculation: number of pills taken/number of pills dispensed. Anticoagulation adherence was assessed at day 30 and end of treatment. Measurements of <80% were considered non-adherent.
Results: Forty patients were enrolled and data is available for 39. Twenty patients were randomized to apixaban with mean age 59 years; 19 patients were randomized to rivaroxaban and had mean age of 64 years.
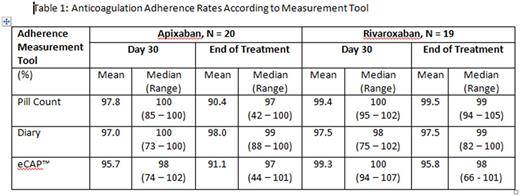
In patients receiving twice daily apixaban, all adherence tools demonstrated similar anticoagulation adherence rates at day 30 follow up with mean of 95.7% for eCAP™, 97% for diaries, and 97.8% by pill count. End of treatment measures were also similar: 91.1%, 98%, and 90.4%, respectively. All three tools showed comparable adherence rates at 30 days with mean of 99.3% by eCAP™, 97.5% with diaries, and 99.4% by pill counts in patients on rivaroxaban treatment. By end of treatment, anticoagulation adherence rates were similar between different measurement tools: 95.8%, 97.5%, and 99.5%, respectively (Table 1).
Conclusions:
In patients with acute VTE, anticoagulation adherence rates were comparable regardless of the adherence assessment tool used. We also demonstrated that simple tools such as medication diaries and pill counts are comparable to expensive electronic device measures.
Castellucci: BMS: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria; Leo Pharma: Honoraria; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria. Le Gal: Bayer: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal